Product Description
Key attributes
Other attributes
Applicable Industries
Manufacturing Plant, Construction works , Energy & Mining
Weight (KG)
3000
Showroom Location
None
Video outgoing-inspection
Provided
Machinery Test Report
Provided
Marketing Type
Ordinary Product
Warranty of core components
Not Available
Core Components
Gear, Ring Gear
Place of CHINAMFG
ZheJiang , China
Condition
New
Warranty
1year
Shape
Ring Gear
Standard or Nonstandard
Nonstandard
Tooth Profile
Helical Gear,spur gear
Material
Steel
Processing
Forging
Pressure Angle
custom
Brand Name
TS
Product Name
Large Ring Gear
Module No.
5-180
Process
Milling,hobbing
Surface treatment
as request
Heat treatment
Q&T
Application
Industry machinery,transmission equipment
Standard
DIN ANSI ISO
Certificate
ISO
OEM Service
YES
Delivery time
15-60days
Packaging and delivery
Packaging Details
Package adapting to CHINAMFG transport
Port
ZheJiang ,HangZhou
Supply Ability
Supply Ability
5 Piece/Pieces per Month
OUR WORKSHOPS
OUR EQUIPMENTS
Technology Process
|
Material |
Carbon steel,Alloy steel |
||
|
Structure |
Forging,casting |
||
|
Type of gear |
spur gear,helical gear,Planetary Gear |
||
|
Heat treatment |
Quenching and tempering |
||
|
Process |
forging, rough machining, QT, finish machining |
||
|
Main equipments |
hobbing,CNC machine |
||
|
Module |
up to 200 |
||
|
Precision of gear |
Grinding ISO Grade 5-7 & Hobbing ISO Grade 8-9 |
||
|
Inspection |
Raw material inspection, UT,physical property test,dimension inspect |
||
|
Application |
Mining machinery, mill, kiln and other equipment |
||
OUR CERTIFICATE
OUR CUSTOMER FEEDBACK
CONTACT
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industry |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hb190-Hb300 |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
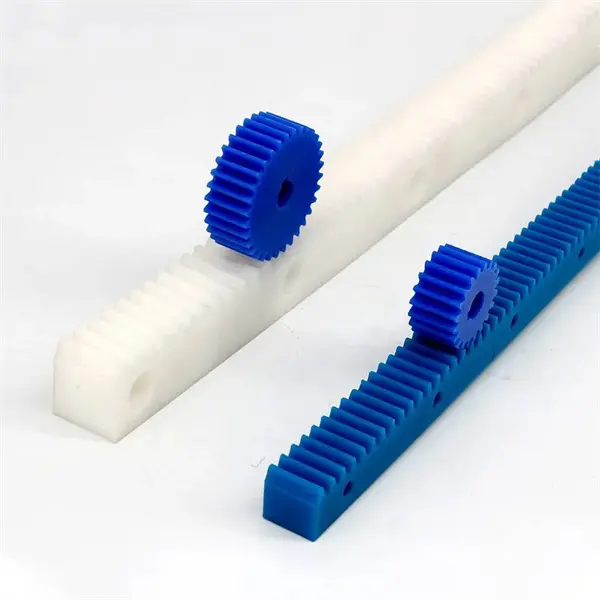

How do rack and pinion systems handle different gear ratios?
Rack and pinion systems can accommodate different gear ratios by adjusting the size and number of teeth on the gears. The gear ratio determines the relationship between the rotational motion of the pinion gear and the linear motion of the rack. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rack and pinion systems handle different gear ratios:
In a rack and pinion system, the pinion gear is a small gear with teeth that meshes with the rack, which is a long, straight bar with teeth along its length. As the pinion gear rotates, it translates rotational motion into linear motion along the rack. The gear ratio is defined as the ratio of the number of teeth on the pinion gear to the number of teeth on the rack. It determines how much linear motion the rack will produce for each revolution of the pinion gear.
To handle different gear ratios, the following approaches can be taken:
- Varying the Number of Teeth: By changing the number of teeth on the pinion gear and the rack, different gear ratios can be achieved. Increasing the number of teeth on the pinion gear relative to the rack will result in a higher gear ratio, providing more linear motion per revolution of the pinion gear. Conversely, reducing the number of teeth on the pinion gear relative to the rack will yield a lower gear ratio, producing less linear motion per revolution of the pinion gear.
- Modifying the Module and Pitch: The module and pitch of the gear teeth can also be adjusted to accommodate different gear ratios. The module refers to the size of the teeth, while the pitch determines the spacing between the teeth. Changing the module and pitch can alter the gear ratio without significantly affecting the overall dimensions of the rack and pinion system. This approach allows for more flexibility in achieving specific gear ratios while maintaining compatibility with existing system components.
- Using Gear Reduction or Multi-Stage Systems: In certain applications where a wide range of gear ratios is required, gear reduction or multi-stage systems can be employed. Gear reduction involves incorporating additional gears between the pinion and the rack to achieve the desired gear ratio. Each additional gear stage introduces its own gear ratio, allowing for more precise control over the system’s overall gear ratio. This approach is commonly used in applications that require high precision or a wide range of motion control options.
The selection of a specific gear ratio depends on the application requirements, such as the desired linear speed, torque, or positional accuracy. The gear ratio determines the system’s speed and force transmission characteristics, as well as its ability to handle different loads. It is important to note that changing the gear ratio can affect other system parameters, such as backlash, efficiency, and system dynamics. Therefore, careful consideration and analysis of the application’s needs and trade-offs are necessary when selecting and adjusting the gear ratio in a rack and pinion system.
How do rack and pinion systems handle variations in temperature and humidity?
Rack and pinion systems are designed to handle variations in temperature and humidity, ensuring their proper functioning and longevity in diverse environmental conditions. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Temperature Variations:
Rack and pinion systems are typically constructed using materials that can withstand a wide range of temperatures. Some common materials used for rack and pinion components include steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and various engineering plastics. These materials are chosen for their thermal stability and resistance to expansion or contraction due to temperature changes.
When exposed to temperature variations, rack and pinion systems can experience dimensional changes. However, the materials used are selected to minimize the effects of thermal expansion or contraction. Manufacturers consider the coefficient of thermal expansion of the materials and design the system with appropriate tolerances to accommodate temperature-related dimensional changes. This helps maintain the system’s accuracy and functionality over a range of operating temperatures.
In extreme temperature conditions, lubrication becomes an important consideration. High temperatures can cause lubricants to degrade, leading to increased friction and wear. To address this, specialized lubricants that can withstand elevated temperatures are used in rack and pinion systems operating in high-temperature environments. Additionally, regular maintenance and lubrication checks are recommended to ensure optimal performance and to mitigate any adverse effects of temperature variations.
Humidity and Moisture:
Humidity and moisture can affect the performance and durability of rack and pinion systems, particularly if the system is exposed to excessive moisture or operates in highly humid environments. Here are some measures taken to address these challenges:
1. Material Selection: The materials used in rack and pinion systems are often chosen for their resistance to corrosion and moisture absorption. Stainless steel, for example, is commonly used due to its excellent corrosion resistance. Similarly, certain types of engineering plastics are less susceptible to moisture absorption, making them suitable for humid environments.
2. Protective Coatings: Applying protective coatings on rack and pinion components can help enhance their resistance to moisture and corrosion. Coatings such as zinc plating, chrome plating, or specialized corrosion-resistant coatings provide an additional barrier against moisture penetration and prolong the system’s lifespan.
3. Sealing and Gasketing: Rack and pinion systems can be designed with sealing mechanisms or gaskets to prevent moisture ingress. Seals and gaskets are placed at critical points, such as the gear meshing area or the housing joints, to create a barrier against moisture and contaminants. These seals help maintain the integrity of the system, reduce the risk of corrosion, and ensure consistent performance even in humid conditions.
4. Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance practices, including cleaning, inspection, and lubrication, are essential for rack and pinion systems exposed to humidity. Cleaning the system to remove any accumulated dirt or moisture, inspecting for signs of corrosion or wear, and applying appropriate lubrication can help mitigate the effects of moisture and ensure the system’s optimal performance and longevity.
By incorporating suitable materials, protective coatings, sealing mechanisms, and maintenance practices, rack and pinion systems can effectively handle variations in temperature and humidity. These measures help maintain the system’s accuracy, reliability, and durability, even in challenging environmental conditions.
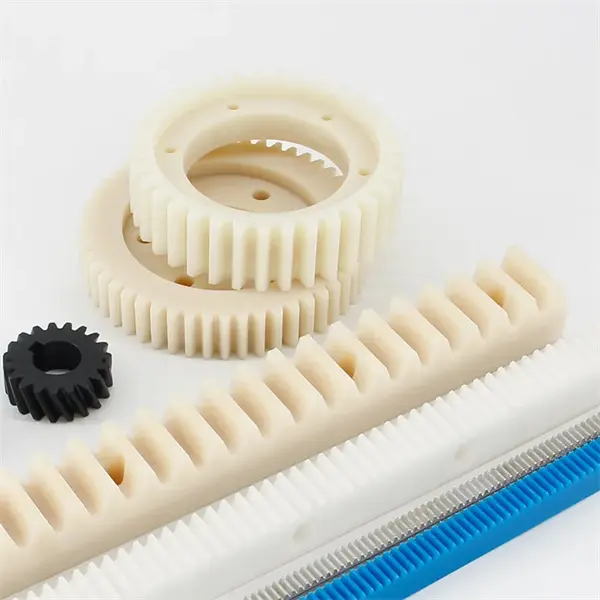

What are the key components of a rack and pinion mechanism?
A rack and pinion mechanism consists of several key components that work together to convert rotational motion into linear motion. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key components of a rack and pinion mechanism:
- Rack: The rack is a linear gear with teeth along its length. It is a long, straight bar that serves as the linear motion component of the mechanism. The rack is often made of metal or plastic and is designed with precision to ensure smooth engagement with the pinion.
- Pinion: The pinion is a small gear with teeth that mesh with the teeth on the rack. It is the rotational motion component of the mechanism. The pinion is typically mounted on a shaft and is connected to a rotary motion source, such as an electric motor or a manual crank.
- Teeth: The teeth on both the rack and the pinion are integral to the mechanism’s operation. The teeth of the pinion mesh with the teeth on the rack, allowing for the transfer of motion. The tooth profile and spacing are crucial for ensuring smooth and efficient engagement between the rack and pinion.
- Bearing Support: To ensure smooth and reliable operation, a rack and pinion mechanism often incorporates bearing support. Bearings are used to support the pinion shaft, reducing friction and allowing for smooth rotation. Bearings may also be used to support the rack, depending on the specific design and application.
- Guides: Guides are used to guide and support the linear motion of the rack. They help maintain alignment and prevent lateral movement or misalignment during operation. Guides can be in the form of rails, tracks, or other structures that keep the rack in the desired path of motion.
- Housing or Mounting Structure: A rack and pinion mechanism may include a housing or mounting structure to provide support, stability, and proper alignment of the components. The housing or structure ensures that the rack and pinion remain securely in place, maintaining the integrity of the mechanism during operation.
- Additional Components: Depending on the specific application, a rack and pinion mechanism may incorporate additional components. These can include lubrication systems to reduce friction and wear, position sensors for feedback and control, and protective covers or enclosures to shield the mechanism from dust, debris, or environmental elements.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the operation of a rack and pinion mechanism, enabling the conversion of rotational motion to linear motion with precision and efficiency.


editor by Dream 2024-05-16